2025
Planner3D: LLM-enhanced Graph Prior Meets 3D Indoor Scene Explicit Regularization
Yao Wei, Martin Renqiang Min, George Vosselman, Li Erran Li, Michael Ying Yang
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) 2025
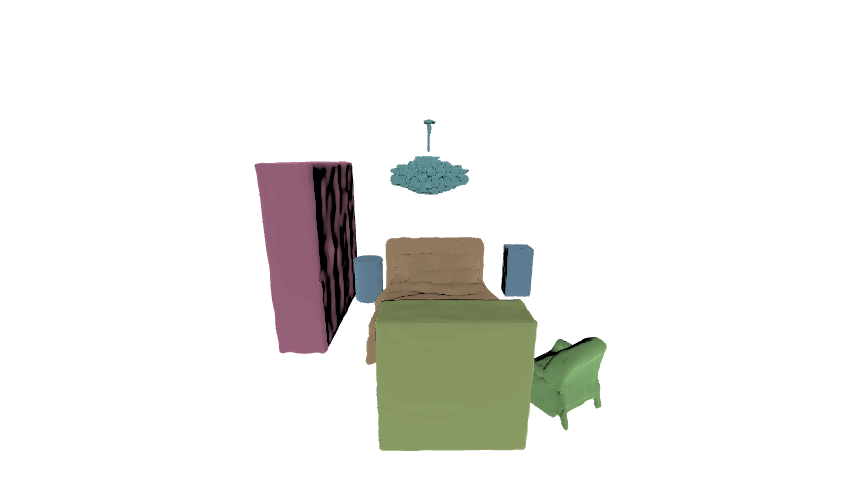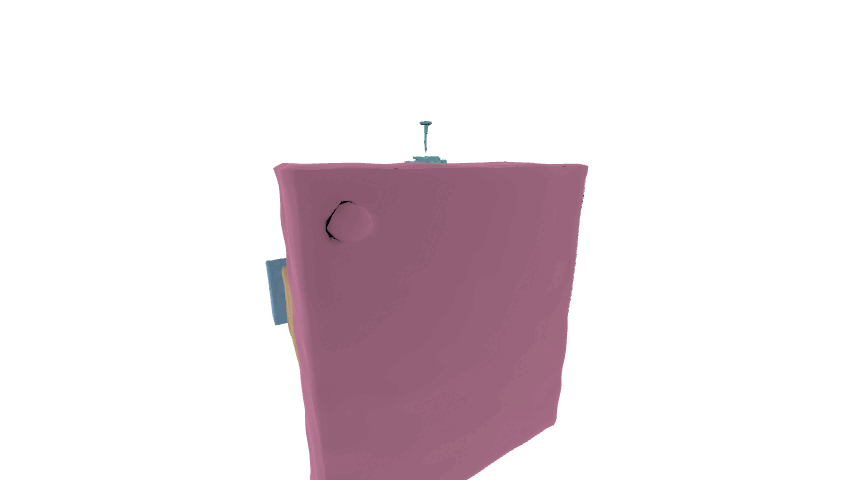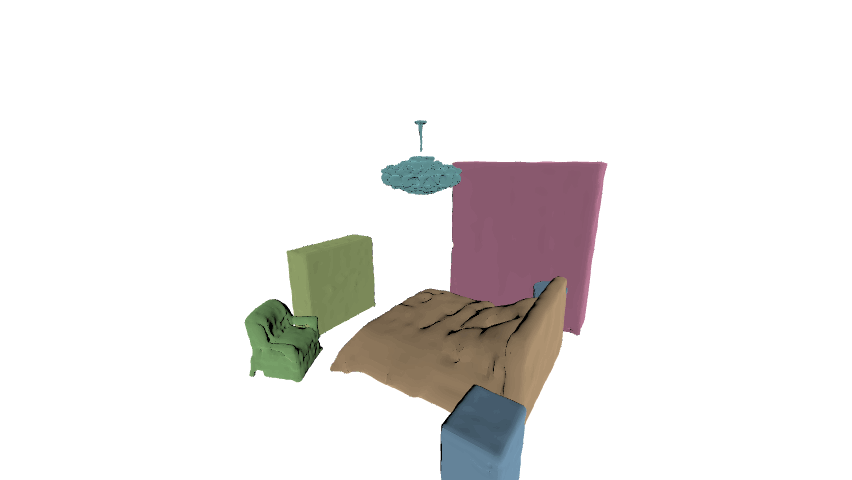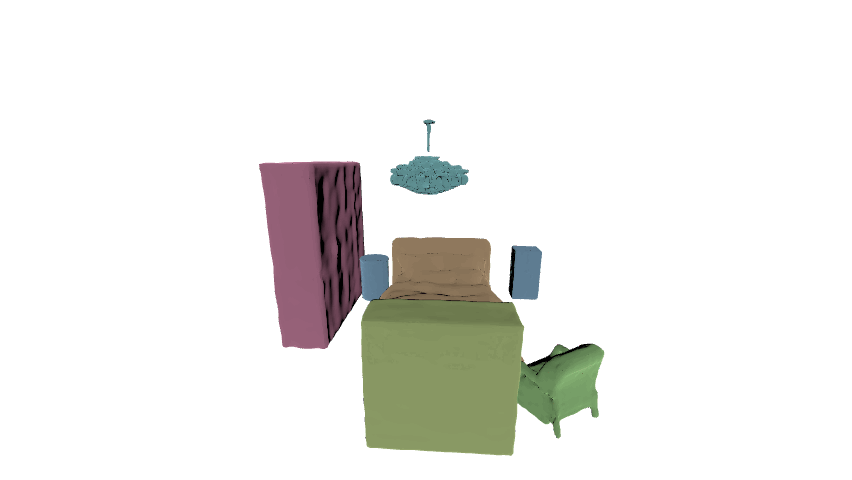
In this paper, we aim at generating realistic and reasonable 3D indoor scenes from scene graph. To enrich the priors of the given scene graph inputs, large language model is utilized to aggregate the global-wise features with local node-wise and edge-wise features. With a unified graph encoder, graph features are extracted to guide joint layout-shape generation. Additional regularization is introduced to explicitly constrain the produced 3D layouts. Benchmarked on the SG-FRONT dataset, our method achieves better 3D scene synthesis, especially in terms of scene-level fidelity.
Planner3D: LLM-enhanced Graph Prior Meets 3D Indoor Scene Explicit Regularization
Yao Wei, Martin Renqiang Min, George Vosselman, Li Erran Li, Michael Ying Yang
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) 2025
In this paper, we aim at generating realistic and reasonable 3D indoor scenes from scene graph. To enrich the priors of the given scene graph inputs, large language model is utilized to aggregate the global-wise features with local node-wise and edge-wise features. With a unified graph encoder, graph features are extracted to guide joint layout-shape generation. Additional regularization is introduced to explicitly constrain the produced 3D layouts. Benchmarked on the SG-FRONT dataset, our method achieves better 3D scene synthesis, especially in terms of scene-level fidelity.
2023
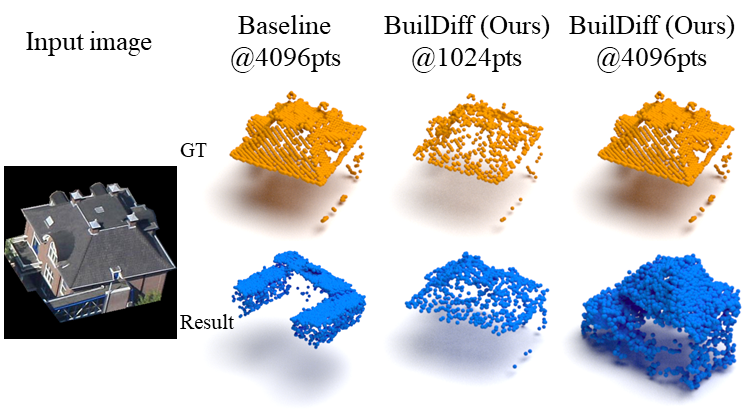
BuilDiff: 3D Building Shape Generation using Single-Image Conditional Point Cloud Diffusion Models
Yao Wei, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW) 2023
We propose a novel 3D building shape generation method exploiting point cloud diffusion models with image conditioning schemes, which demonstrates flexibility to the input images. By cooperating two conditional diffusion models and introducing a regularization strategy during denoising process, our BuilDiff is able to synthesize building roofs while maintaining the overall structures. We validate our framework on two newly built datasets and extensive experiments show that our method outperforms previous works in terms of building generation quality.
BuilDiff: 3D Building Shape Generation using Single-Image Conditional Point Cloud Diffusion Models
Yao Wei, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW) 2023
We propose a novel 3D building shape generation method exploiting point cloud diffusion models with image conditioning schemes, which demonstrates flexibility to the input images. By cooperating two conditional diffusion models and introducing a regularization strategy during denoising process, our BuilDiff is able to synthesize building roofs while maintaining the overall structures. We validate our framework on two newly built datasets and extensive experiments show that our method outperforms previous works in terms of building generation quality.
2022

Flow-based GAN for 3D Point Cloud Generation from a Single Image
Yao Wei, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) 2022
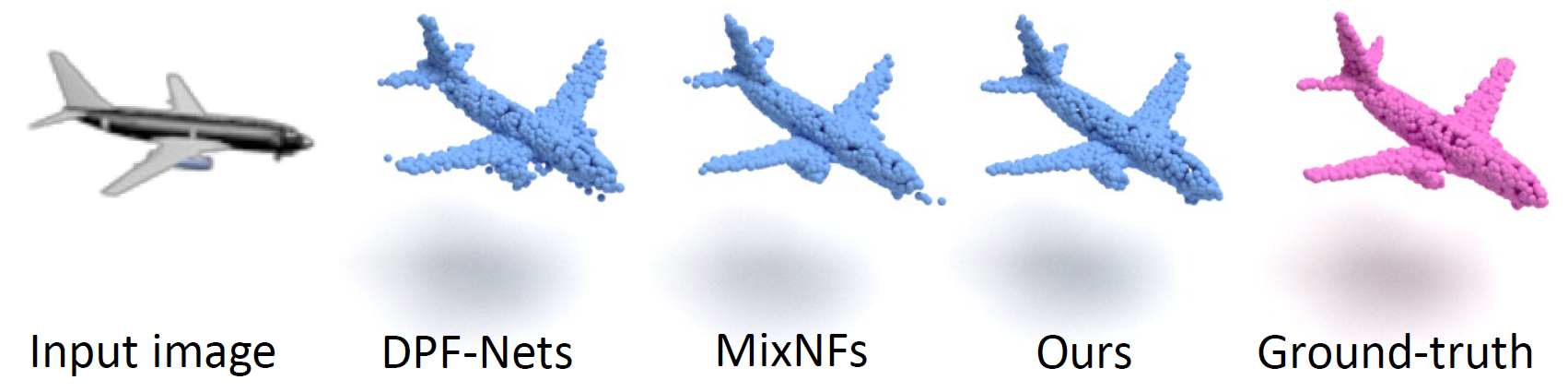
This work introduces a hybrid explicit-implicit generative modeling scheme, which inherits the flow-based explicit generative models for sampling point clouds with arbitrary resolutions while improving the detailed 3D structures of point clouds by leveraging the implicit generative adversarial networks (GANs).
Flow-based GAN for 3D Point Cloud Generation from a Single Image
Yao Wei, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) 2022
This work introduces a hybrid explicit-implicit generative modeling scheme, which inherits the flow-based explicit generative models for sampling point clouds with arbitrary resolutions while improving the detailed 3D structures of point clouds by leveraging the implicit generative adversarial networks (GANs).
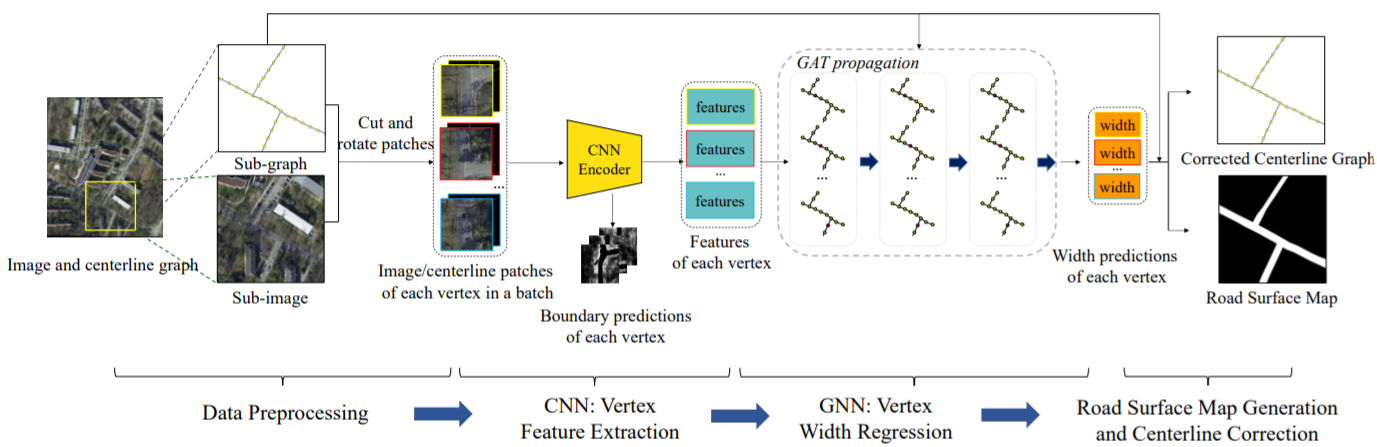
A Combination of Convolutional and Graph Neural Networks for Regularized Road Surface Extraction
Jingjing Yan, Shunping Ji, Yao Wei
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2022
The proposed method comprehensively outperforms the recent CNN-based segmentation methods and other regularization methods in the intersection over union (IoU) and smoothness score, and a visual check shows that a majority of the prediction results of the proposed method approach the human delineation level.
A Combination of Convolutional and Graph Neural Networks for Regularized Road Surface Extraction
Jingjing Yan, Shunping Ji, Yao Wei
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2022
The proposed method comprehensively outperforms the recent CNN-based segmentation methods and other regularization methods in the intersection over union (IoU) and smoothness score, and a visual check shows that a majority of the prediction results of the proposed method approach the human delineation level.
2021
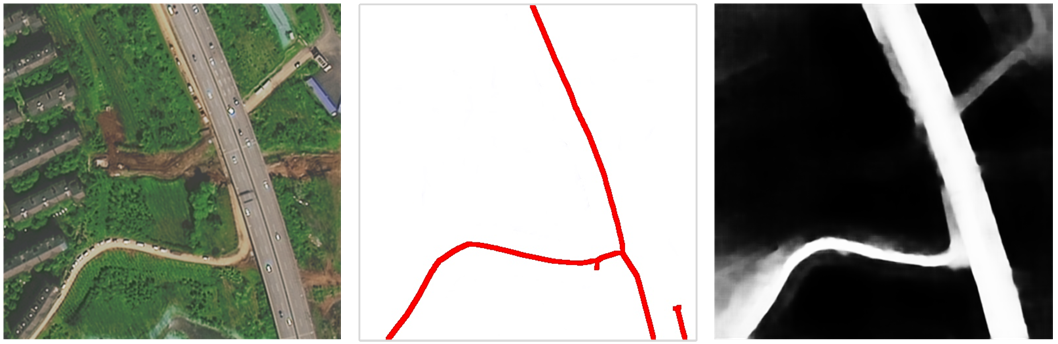
Scribble-based Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for Road Surface Extraction from Remote Sensing Images
Yao Wei, Shunping Ji
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2021 ESI Highly Cited Paper (Top 1%)
A scribble-based weakly supervised road surface extraction method named ScRoadExtractor, which learns from easily accessible scribbles such as centerlines instead of densely annotated road surface ground truths to propagate semantic information from sparse scribbles to unlabeled pixels. The results demonstrate that ScRoadExtractor exceeds the classic scribble-supervised segmentation method by 20% for the intersection over union (IoU) indicator and outperforms the state-of-the-art scribble-based weakly supervised methods at least 4%.
Scribble-based Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for Road Surface Extraction from Remote Sensing Images
Yao Wei, Shunping Ji
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2021 ESI Highly Cited Paper (Top 1%)
A scribble-based weakly supervised road surface extraction method named ScRoadExtractor, which learns from easily accessible scribbles such as centerlines instead of densely annotated road surface ground truths to propagate semantic information from sparse scribbles to unlabeled pixels. The results demonstrate that ScRoadExtractor exceeds the classic scribble-supervised segmentation method by 20% for the intersection over union (IoU) indicator and outperforms the state-of-the-art scribble-based weakly supervised methods at least 4%.
2020
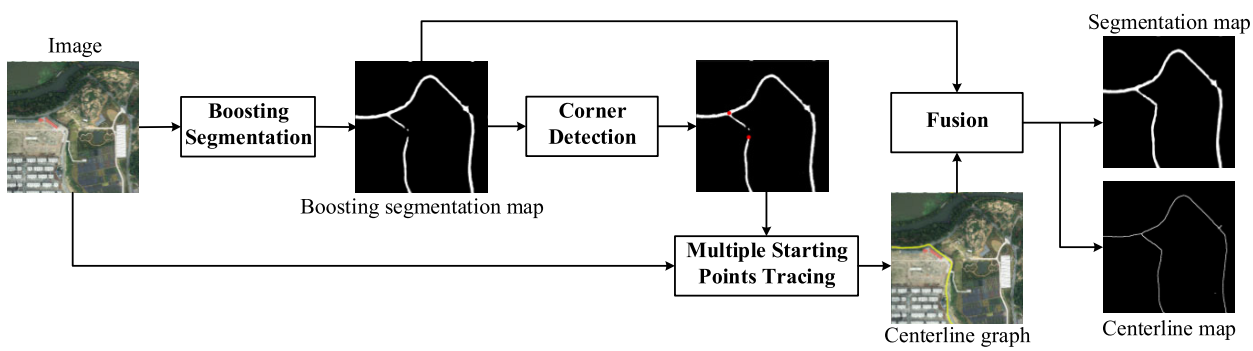
Simultaneous Road Surface and Centerline Extraction From Large-Scale Remote Sensing Images Using CNN-Based Segmentation and Tracing
Yao Wei, Kai Zhang, Shunping Ji
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2020
This article introduces a novel deep learning-based multistage framework to accurately extract the road surface and road centerline simultaneously and demonstrates the superior performance of the proposed framework. Specifically, our method’s performance exceeded the other methods by 7% and 40% for the connectivity indicator for road surface segmentation and for the completeness indicator for centerline extraction, respectively.
Simultaneous Road Surface and Centerline Extraction From Large-Scale Remote Sensing Images Using CNN-Based Segmentation and Tracing
Yao Wei, Kai Zhang, Shunping Ji
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2020
This article introduces a novel deep learning-based multistage framework to accurately extract the road surface and road centerline simultaneously and demonstrates the superior performance of the proposed framework. Specifically, our method’s performance exceeded the other methods by 7% and 40% for the connectivity indicator for road surface segmentation and for the completeness indicator for centerline extraction, respectively.
2019
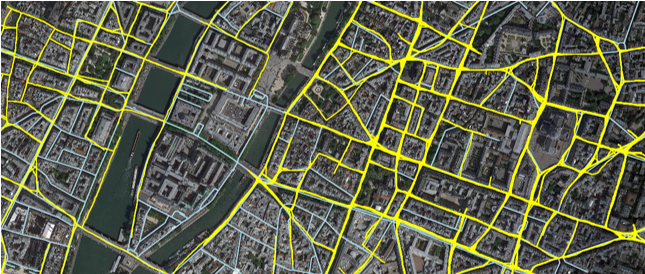
Road Network Extraction from Satellite Images Using CNN Based Segmentation and Tracing
Yao Wei, Kai Zhang, Shunping Ji
IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2019
This work proposes a multiple starting points tracer which benefits from both segmentation and tracing methods, and finds that this method achieves 8% improvement on IoU.
Road Network Extraction from Satellite Images Using CNN Based Segmentation and Tracing
Yao Wei, Kai Zhang, Shunping Ji
IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2019
This work proposes a multiple starting points tracer which benefits from both segmentation and tracing methods, and finds that this method achieves 8% improvement on IoU.